Organization of the presentation of object's attributes on the map |



|
|
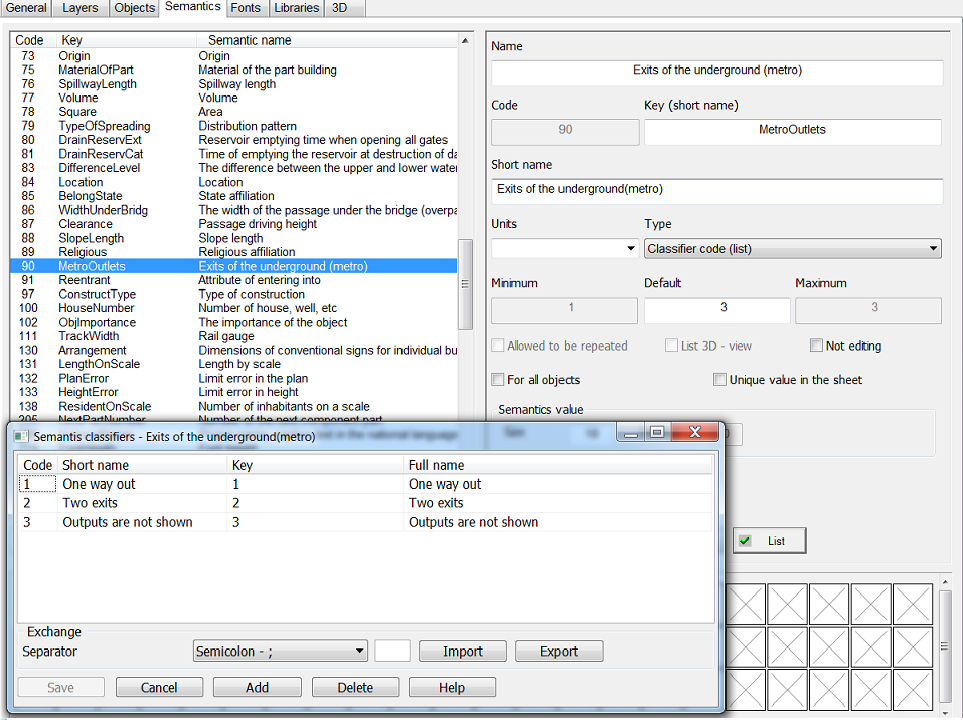
In addition to the spatial description of the object, its individual attributes can also be transferred to the map. The attributive information of the record about the object falls into the semantics of the corresponding map object and can be taken into account when forming a conventional symbol of object on the map. The assignment of certain attributive fields of the database table containing information about the object and the indicating the corresponding semantic characteristics of the cartographic object is performed by the service administrator at the stage of customizing the program. Semantics can be simple or semantics-classifiers (lists). Simple semantics contains value itself that is written into it. This value should correspond to type of data defined for this semantic characteristic in the digital classifier of map objects. Semantics can be of different types: character (string), numeral, pointer to object and name of a file, and others. For semantics of the «numeral» type, default values are entered. These default values are common to all objects. If the semantics is mandatory for the object, and the value is absent for some reason, the semantics of the object will be assigned a default value. When entering values of semantics of objects, the interval of possible values is set according to the minimum and maximum default values. For semantics the unit of measure can be set. Units of measure are used in particular for signatures of semantics values. The size and precision of the semantics field value are used for formatted output of semantics values and for performing information exchange with the database. Semantics-classifier (list) has a type - a code from classifier, which means that the semantics values are integers, which are assigned symbolic values. For such semantics, a list is pre-filled where the correspondence of numeric values to character strings has been specified. The semantics-classifier stores the numeric
code of the record, which is defined in the list of possible semantics values. The list itself is stored in the digital classifier of map objects. When updating the map based on information from the database, the program automatically determines the type of semantic characteristic associated with the attribute field of the database table. If the semantics is a semantics-classifier, then the program selects the recording code from the list of possible values of this semantics. The selection is carried out according to the value of the attribute field of the database table corresponding to this semantics. The search for a record in the list of possible semantics values is carried out by matching the value of the attribute field both with the key value in the list and with the character values of this list themselves. Thus, the fields of the database tables associated with the semantics--classifiers can contain either key values from the list of acceptable semantics values, or these values themselves (decoded strings).
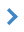
Example of a list of values for semantics-classifier:
|